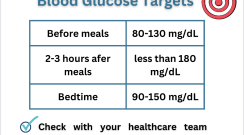
- Posted: 26 June 2023
Managing diabetes during the summer months requires some additional considerations due to the potential impact of heat, increased physical activity, and changes in routine. Here are some tips to help you manage your diabetes effectively during this season.